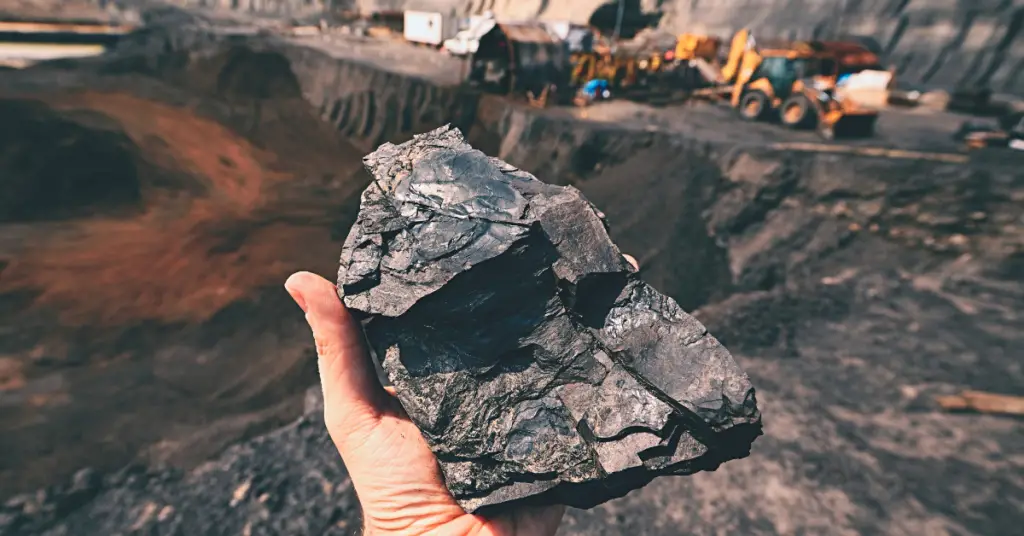
Non-renewable fuels have helped drive the growth of modern society, particularly by providing the ability to industrialize and transport people and materials from one place to another. They exist in infinite number and cannot easily be replenished. They took a long time to create and the people are using them far faster than Earth can produce them.
Oil: Oil is currently overwhelmingly the fuel of choice for vehicles, and many scientists agree that oil may only last 40 to 50 years if it continues to be used at current and increasing rates., but even some oil companies agree. However, this is not the only supply problem: there is also the problem of access to oil. In the US, oil accounts for more than 40 percent of the nation’s total energy consumption.
However, oil and other petroleum products are more than just a source of energy and are also sources of political power and controversy . An Important Mission of the US Department of Energy’s Fossil Fuels Office is so vital to the continued well-functioning of the country. For this reason, oil is stored at key locations in the United States.
However, many supplies of oil, which are relatively easy and cheap to come by, are running out, so oil companies and the government are trying to figure out how to eliminate the rest without colliding with the price of oil soaring so high that it devastates the economy.
Coal : More than half of the power plants in the United States burn coal, which has traditionally had a very dirty reputation. Burning coal produces not only carbon dioxide but also sulfur and nitrogen side products that can cause smog and acid rain. The Process of Mining coal also pollutes the environment, whether underground or surface and poses a significant health and safety hazard to miners.
While coal is a non-renewable resource, reserves in the US can likely meet the nation’s energy needs for the next 200 to 300 years, giving ample time to figure out how to replace it. More important in the short term is figuring out how to burn coal without producing polluting gases.
According to the DOE, the US has a quarter of the world’s coal reserves, and that quarter contains more energy than the world’s recoverable oil reserves. Coal is a huge potential energy source for the nation, which is why finding and implementing ways to burn it cleaner is so important.
Uranium: Nearly 20 percent of all electricity generated in the United States is generated by coal as a source of energy. Nuclear power works by harnessing the energy released when a uranium atom breaks apart; Fossil fuels are not burned, so there are no greenhouse gas emissions. However, the uranium enrichment method, which is required to convert heavy Metal to usable fuel , releases carbon dioxide.
Moreover, the question remains of what to do with spent uranium, which is radioactive and highly carcinogenic. Nuclear waste is currently sealed and stored, and there are plans to build a large underground facility where the waste can be transported and then stored indefinitely. An accident or even sabotage in a nuclear reactor can have catastrophic consequences.
Natural Gas: According to the DOE, approximately 22% of the country’s energy consumption comes from natural sources. More than half of the nation’s homes use natural gas as their main heating fuel. When natural gas burns, it emits far fewer greenhouse gas emissions than coal. Natural gas is also considered a cleaner fuel than oil, which is one of the reasons why why 900 of the next 1,000 powerplants built in the U.S. will run on natural gas.
Although natural gas is cleaner burning than coal and oil, it still releases carbon dioxide when it burns. Gas still has its issues, among them the release of its main ingredient (the greenhouse gas methane) during production, storage, and transport and the potential for natural gas to explode when high concentrations come into contact with a spark.
One of the great examples of how humanity directly impacts the planet (and indirectly affects itself) is waste, whether it comes from a factory smokestack is consigned to a landfill or incinerator, because of its potential to pollute the atmosphere, the land, and the water.
The burning of fossil fuels is perhaps the greatest contributor to pollution, yet it’s currently the primary means for generating and transporting energy.
Electricity, for example, is one of the most popular forms of energy provided around the world. The cheapest and most reliable way of providing electricity to cities and towns involves power generation plants that burn fossil fuels such as coal. The energy needed to transport the coal to the power plant comes from refining oil, which is also a fossil fuel. In the end, the combustion of fossil fuels causes much of the greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
When fossil fuels are burned, sulfur, nitrogen, and carbon combine with oxygen to form compounds called oxides.In landfills or incinerators, their components must be treated to avoid emitting potentially toxic chemicals into the ground and air.
True, new landfills are carefully sealed so that their contents don’t leak, and incinerators use much cleaner technology than they once did. But all of this requires energy, which is exactly what people around the world should consume less of.
In developing countries, the waste issue is focused more on a lack of infrastructure and facilities, meaning that garbage may be dumped in any spare piece of land or in landfill sites that fail to protect the environment, or it may be burned without consideration for either nearby residents or the environment. This pollution aggravates health and hygiene problems as it risks contaminating soils, local water sources, and the air.

Erzsebet Frey (Eli Frey) is an ecologist and online entrepreneur with a Master of Science in Ecology from the University of Belgrade. Originally from Serbia, she has lived in Sri Lanka since 2017. Eli has worked internationally in countries like Oman, Brazil, Germany, and Sri Lanka. In 2018, she expanded into SEO and blogging, completing courses from UC Davis and Edinburgh. Eli has founded multiple websites focused on biology, ecology, environmental science, sustainable and simple living, and outdoor activities. She enjoys creating nature and simple living videos on YouTube and participates in speleology, diving, and hiking.