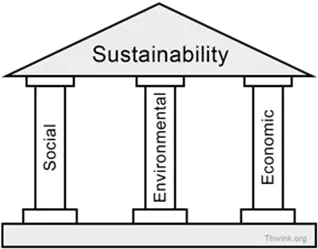
The principle of the three pillars of sustainability states that in order to fully solve the problem of sustainability, each of the three pillars of sustainability must be balanced. The three pillars are social sustainability, ecological sustainability and economic sustainability.
Social Sustainability
Social sustainability is about identifying and managing the positive and negative business impacts on people.
The first six principles of the United Nations Global Compact focus on this social dimension of corporate sustainability, of which human rights are a cornerstone. Their social sustainability work also encompasses the human rights of specific groups: labour, women’s empowerment and gender equality, children, indigenous peoples, people with disabilities, as well as people-centered approaches to the impact of business on poverty. In addition to groups of rights holders, social sustainability also includes issues that affect them, such as education and health.
In this current scenario, the environment has become a major constraint on human progress. The fundamental importance is social sustainability. Education against poverty is the main goal of sustainable development. The man in hunger focuses on food rather than environmental awareness. Henceforth, poverty education must pass through qualitative development, redistribution, and division of population stability and social conviviality rather than through increased performance.
Economic sustainability
Economic sustainability refers to practices that support long-term economic growth without adversely affecting the social, environmental, and cultural aspects of the community. Human communities around the world can maintain their independence and have access to the financial and other resources they need to meet their needs.
The economic systems are intact and the activities are available to everyone as a secure livelihood. Universal human rights and basic needs are available to all people who have access to sufficient resources to keep their families and communities healthy and safe. Healthy communities have fair leaders who ensure that personal, labor and cultural rights are respected and all people are protected from discrimination.
Ecological sustainability
It is necessary for people and has its origin in social issues. It itself is supposed to improve human well-being by protecting the sources of raw materials for human needs and ensuring that they are not used, reducing human waste in order to avoid harm to humans.
Humanity must learn to live within the limits of the biophysical environment. Ecological integrity is preserved, all environmental systems of the earth are kept in balance, while the natural resources contained therein are consumed by humans to an extent to which they can be restored.

Erzsebet Frey (Eli Frey) is an ecologist and online entrepreneur with a Master of Science in Ecology from the University of Belgrade. Originally from Serbia, she has lived in Sri Lanka since 2017. Eli has worked internationally in countries like Oman, Brazil, Germany, and Sri Lanka. In 2018, she expanded into SEO and blogging, completing courses from UC Davis and Edinburgh. Eli has founded multiple websites focused on biology, ecology, environmental science, sustainable and simple living, and outdoor activities. She enjoys creating nature and simple living videos on YouTube and participates in speleology, diving, and hiking.